Collection: C - C Collection
Series:
Folder:
0000.000
Item:
1841_00001
Title:
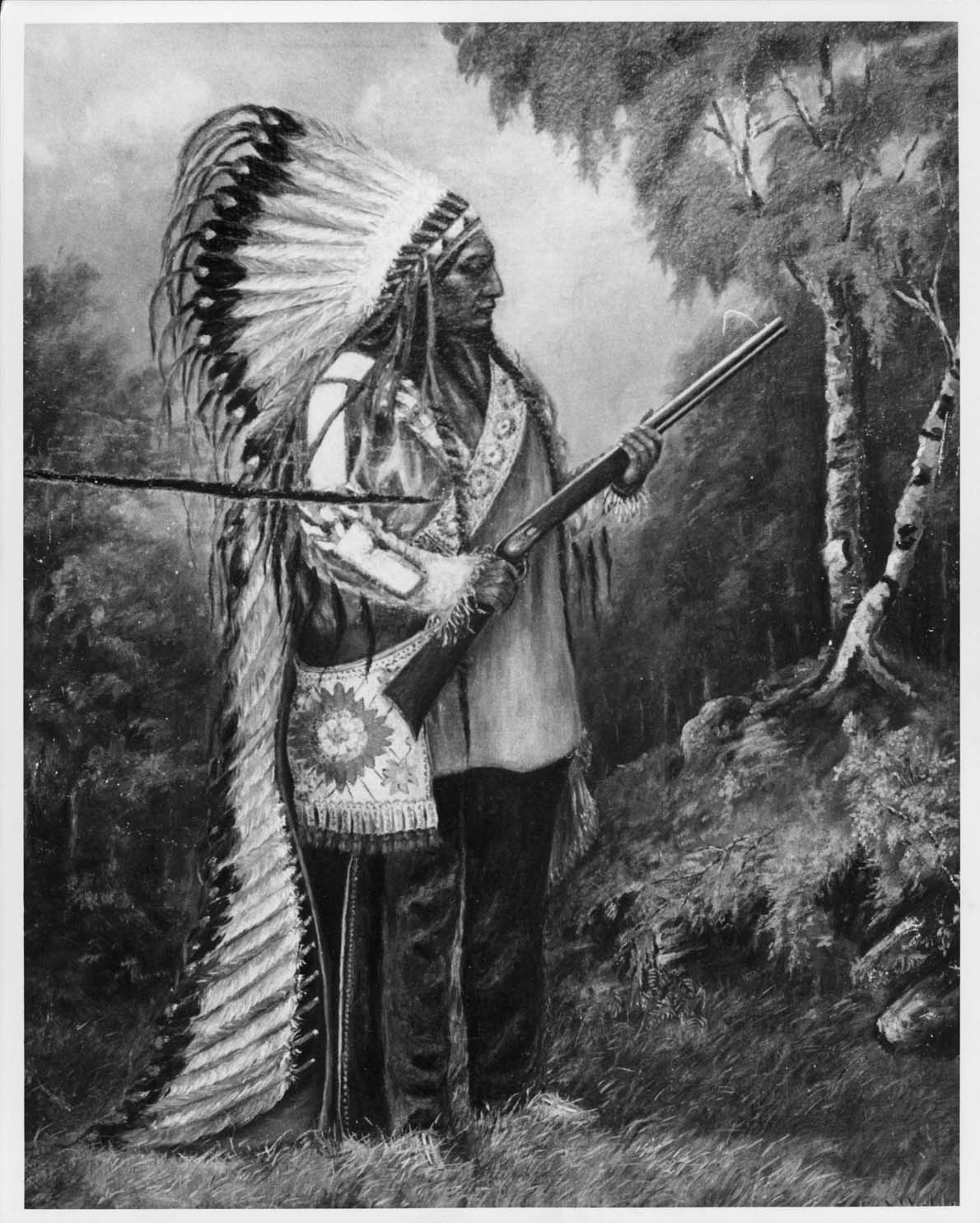
Sitting Bull painting by Catherine (Caroline) Weldon
Date:
1890
Creator:
Inscription/Marks:
Summary:
Full length studio portrait of Sitting Bull, Dakota Chief, wearing war bonnet, holding gun, standing in front of painted backdrop. The canvas is slashed open on left side. Copy of original colour painting Museum SHSND 12319. __Biographical Sketch by Daniel Guggisberg, historian, Santa Fe, NM © 2011-2016
Caroline Weldon (December 4, 1844 - March, 15 1921) was a 19th-century artist and activist with the National Indian Defense Association. Weldon became a confidante and the personal secretary to the legendary Lakota Sioux Indian leader Sitting Bull during the time when Plains Indians had adopted the Ghost Dance movement.
Early life and education
Caroline Weldon was born Susanna Carolina Faesch on December 4th 1844 in Klein-Basel, Canton Basel, Switzerland [10]. Her father was Johann Lukas Faesch, a career Swiss mercenary military officer serving in a Swiss regiment in France; her mother was Anna Maria Barbara, née Marti. She arrived in America in 1852 at the age of 8 years, together with her mother, settling in Brooklyn, Kings County, New York. That year, her mother was remarried to the exiled German revolutionary, Dr. Karl Heinrich Valentiny who ran a medical practice in Brooklyn. There on May 30th 1866 Susanna Carolina Faesch was married to Dr. Bernhard Claudius Schlatter, a physician and fellow Swiss. Her marriage to Dr. Schlatter remained childless and was an unhappy one. In June 1876 she ran away with a married man identified in court records as Christopher J. Stevenson and lived briefly in a rented apartment in Hoboken NJ and by whom she had a child born later that year or early 1877, a boy she named Christie. Her relationship with Stevenson however did not last for he would soon abandon her to return to his wife of many years, whereas she ended up returning to Brooklyn to move in to live with her mother and stepfather. Her marriage to Dr. Schlatter was formally divorced in 1883. [1], [2], [11]
Career
Weldon pursued her interests in art. After her divorce on July 18th 1883 from Dr. Schlatter and having been abandoned by Stevenson, she became committed to the cause of Native Americans. Upon the death of her mother in April 1887 she had inherited some money which gave her the means to freely pursue her interests. Sometimes thereafter she changed her name to Caroline Weldon, presumably to allow her to put her past behind her, although her exact reasons for this action remain unknown. In the summer of 1889 Caroline Weldon traveled to Dakota Territory to fulfill her dream of living among the Sioux. She had joined NIDA, the National Indian Defense Association, headed by Dr. Thomas Bland and his wife Dr. Cora Bland, embarking on a quest to aid the Sioux in their struggle to fight the US government’s attempt under the Dawes Act to expropriate vast portions of the Great Sioux Reservation for the purpose of opening same up for white settlement and with the intent of rendering the creations of the two new states of North Dakota and South Dakota economically viable. She befriended Sitting Bull, leader of the traditionalist faction among the Sioux acting as his secretary, interpreter and advocate. After she had moved to live at Sitting Bull’s compound on the Grand River at Standing Rock Indian Reservation with her young son Christie, her confrontations and open defiance of Indian Agent James McLaughlin did not endear her to the general public, causing the latter to initiate a smear campaign, resulting in her being hated and reviled by much of the white community and vilified in the national press. When in summer of 1890, the Ghost Dance Movement swept through the Indian Reservations of the West; she denounced it and warned Sitting Bull that it would give the government an excuse to harm him and summon the military for intervention against his people that would result in the destruction of the Sioux Nation. Sitting Bull turned against her and upon her son Christie falling ill in November of that year, she decided to leave. The subsequent events of Sitting Bull’s murder and the Wounded Knee Massacre the following December proved her right, adding to her sense of futility and failure. Her son Christie died on November 19th 1890 near Pierre on the riverboat Chaska while on her way to her new home in Kansas City, MO. She lived briefly in the latter city with her nephew Friedrich William Schleicher, a school teacher, only to return eventually to Brooklyn, NY. She disappeared into obscurity soon after. [3], [4], [5], [6], [7], [8], [11]
Weldon also painted four portraits of the chief, of which two have survived. One is now held by the North Dakota Historical Society in Bismarck, ND and the other by the Historic Arkansas Museum in Little Rock, AR.
Later life
Weldon died alone in her Brooklyn apartment on 15 March 1921. The cause of death was accidental third degree burns from a candle to her face and body. She was interred at the Valentiny family plot at Green Wood Cemetery in Brooklyn, NY - Lot 13387, Section 41. [9], [11]
In popular culture
The poet and playwright Derek Walcott refers to Weldon and her life in his play “The Ghost Dance” and in his epic poem “Omeros”. He features Native American history together with that of the demise of the Native Arawak people in St. Lucia, in the Caribbean.
The motion picture “Woman Walks Ahead” 2017 by Bedford Falls Productions, Santa Monica, CA starring Jessica Chastain and Michael Greyeyes, directed by Susanna White, chronicles Weldon's life among the Sioux. It must be noted that in typical Hollywood fashion the film’s script authors took considerable artistic license rendering the overall story depicted therein as far from historical reality.
Sources
[1] Superior Court, New York County, volume 62, pp. 177 ff. Divorce Record Schlatter vs. Schlatter 1883, New York State Supreme Court, Civil Branch, 31 Chamber Street, 7th Floor, New York NY 10007
[2] Caroline Weldon genealogy http://worldconnect.rootsweb.ancestry.com/cgi-bin/igm.cgi?op=GET&db=caroline_weldon&id=I03
[3] Pollack, Eileen. Woman Walking Ahead: In Search of Catherine Weldon and Sitting Bull. Albuquerque: University of New Mexico Press, 2002
[4] Richardson, Heather Cox. Wounded Knee: Party Politics and the Road to an American Massacre. New York: Basic Books, 2010
[5] McLaughlin, James. 1910. My Friend the Indian http://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=loc.ark:/13960/t00008872;view=1up;seq=11
[6] Matteoni, Norman E. Prairie Man. The Struggle between Sitting Bull and Indian Agent James McLaughlin. Guilford CT: 2015
[7] Stanley Vestal Papers, University of Oklahoma Library Archives, Prof. Walter Stanley Campbell (1877-1957) https://digital.libraries.ou.edu/whc/nam/collection.asp?cID=1224&sID=7
[8] Vestal, Stanley (aka Campbell, Walter Stanley). New Sources of Indian History 1850-1891, University of Oklahoma Press, Norman, OK, 1934; transcripts of letters written by Caroline Weldon
[9] Caroline Weldon burial site. http://www.findagrave.com/cgi-bin/fg.cgi?page=gr&GSln=Weldon&GSfn=Susanna&GSbyrel=all&GSdyrel=all&GSob=n&GRid=57225492&df=all&
[10] Faesch Familienarchiv, Staatsarchiv des Kantons Basel, Basel, Switzerland, (Ref. StABS, PA397a, Gerichtsarchiv U152, Uc7)
[11] extensive research notes Daniel Guggisberg, Historian, Santa Fe NM © 2011-2016
Red ID: PH_I_89462 Image ID: 51485 Image Notes: C1841-00001